
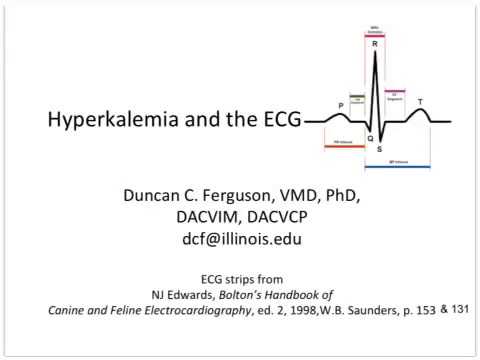
Hyperventilation may indicate a compensatory response to metabolic acidosis, which is one of the possible causes of hyperkalemia. Occasionally palpitations and shortness of breath may occur. Nonspecific symptoms may include feeling tired, numbness and weakness. The symptoms of an elevated potassium level are generally few and nonspecific.

The word hyperkalemia comes from hyper- 'high' + kalium 'potassium' + -emia 'blood condition'. It is associated with an increased mortality, whether due to hyperkalaemia itself or as a marker of severe illness, especially in those without chronic kidney disease. Among those who are hospitalized, rates are between 1% and 2.5%. Hyperkalemia is rare among those who are otherwise healthy. Hemodialysis is the most effective method. Measures to remove potassium from the body include diuretics such as furosemide, potassium-binders such as polystyrene sulfonate and sodium zirconium cyclosilicate, and hemodialysis. Medications that might worsen the condition should be stopped and a low potassium diet should be started. Other medications used to rapidly reduce blood potassium levels include insulin with dextrose, salbutamol, and sodium bicarbonate. Initial treatment in those with ECG changes is salts, such as calcium gluconate or calcium chloride. Pseudohyperkalemia, due to breakdown of cells during or after taking the blood sample, should be ruled out. High levels can be detected on an electrocardiogram (ECG). The severity is divided into mild (5.5–5.9 mmol/L), moderate (6.0–6.4 mmol/L), and severe (>6.5 mmol/L). A number of medications can also cause high blood potassium including spironolactone, NSAIDs, and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors. Ĭommon causes of hyperkalemia include kidney failure, hypoaldosteronism, and rhabdomyolysis. Hyperkalemia can cause an abnormal heart rhythm which can result in cardiac arrest and death. Occasionally when severe it can cause palpitations, muscle pain, muscle weakness, or numbness. Typically hyperkalemia does not cause symptoms. Normal potassium levels are between 3.5 and 5.0 mmol/L (3.5 and 5.0 mEq/L) with levels above 5.5 mmol/L defined as hyperkalemia. Hyperkalemia is an elevated level of potassium (K +) in the blood. Medications, low potassium diet, hemodialysis Ĭalcium gluconate, dextrose with insulin, salbutamol, sodium bicarbonate

Kidney failure, hypoaldosteronism, rhabdomyolysis, certain medications īlood potassium > 5.5 mmol/L, electrocardiogram Palpitations, muscle pain, muscle weakness, numbness


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
